Piggy - BTL1 PCAP Analysis Lab

🎯 Lab Objective
Scenario: Investigate network activity across four PCAP files to identify data exfiltration, malware infrastructure, and attacker techniques.
Skills Practiced:
- PCAP analysis with Wireshark
- SSH traffic analysis
- OSINT and threat intelligence research
- ASN attribution
- MITRE ATT&CK framework mapping
Tools Used:
- Wireshark
- VirusTotal
- WHOIS/ASN lookups
- MITRE ATT&CK Navigator
📊 Investigation Summary
Platform: Security Blue Team (BTL1 Certification Preparation)
Category: Network Security Monitoring - Foundational Skills
Lab Focus: Multi-PCAP investigation, data exfiltration analysis, threat intelligence
Completion Date: February 13, 2026
Score: 27/27 points
Tags: Wireshark SSH OSINT ATTACK BTL1
🔍 PCAP One: SSH Data Exfiltration
Question 1: Remote SSH IP Address
What remote IP address was used to transfer data over SSH? (Format: X.X.X.X)
Analysis:
Applied SSH filter in Wireshark to identify encrypted data transfer sessions.
Methodology:
- Applied filter:
tcp.port == 22 - Reviewed TCP conversations
- Identified remote endpoint for SSH session
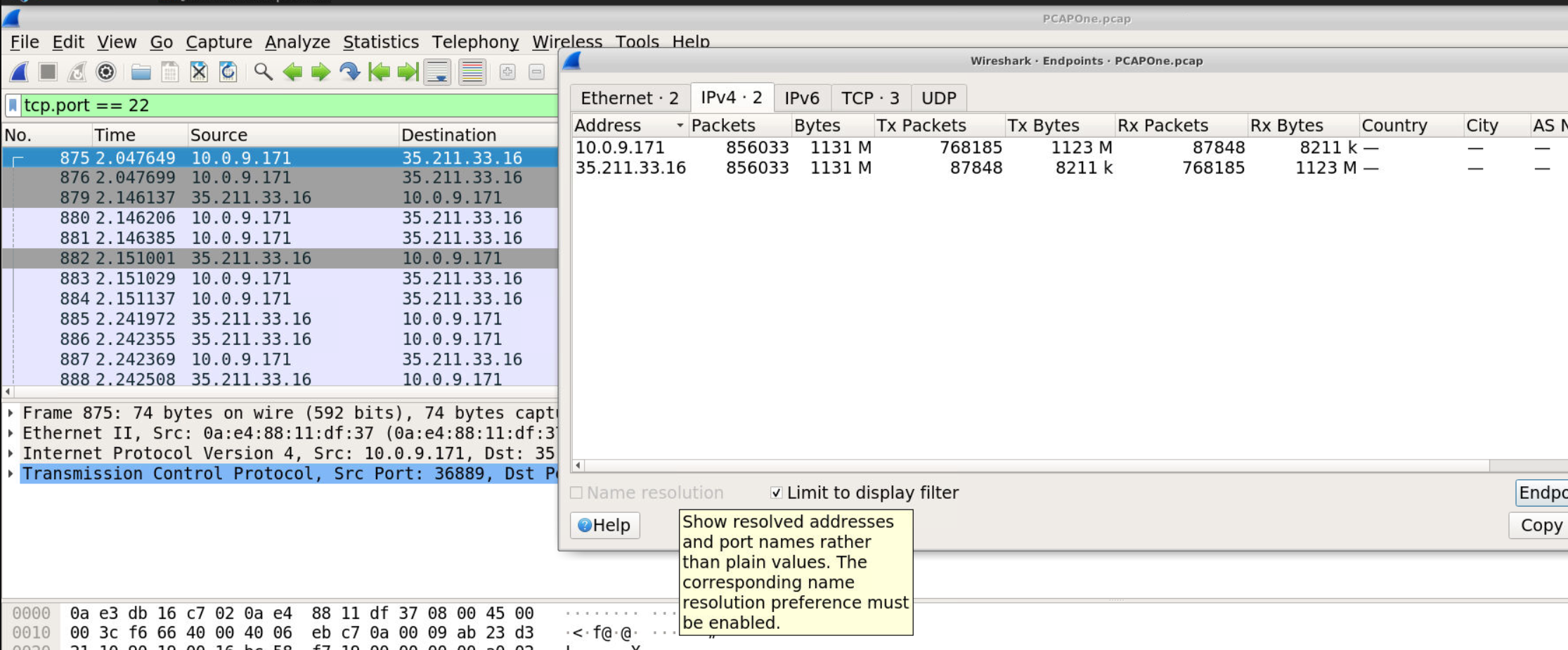
Answer: 35.211.33.16
Question 2: Data Transfer Volume
How much data was transferred in total? (Format: XXXX M)
Analysis:
Used Wireshark’s Statistics feature to calculate total SSH data transfer.
Methodology:
- Statistics → Conversations → IPv4
- Located SSH conversation (35.211.33.16)
- Summed bidirectional traffic (Tx + Rx bytes)
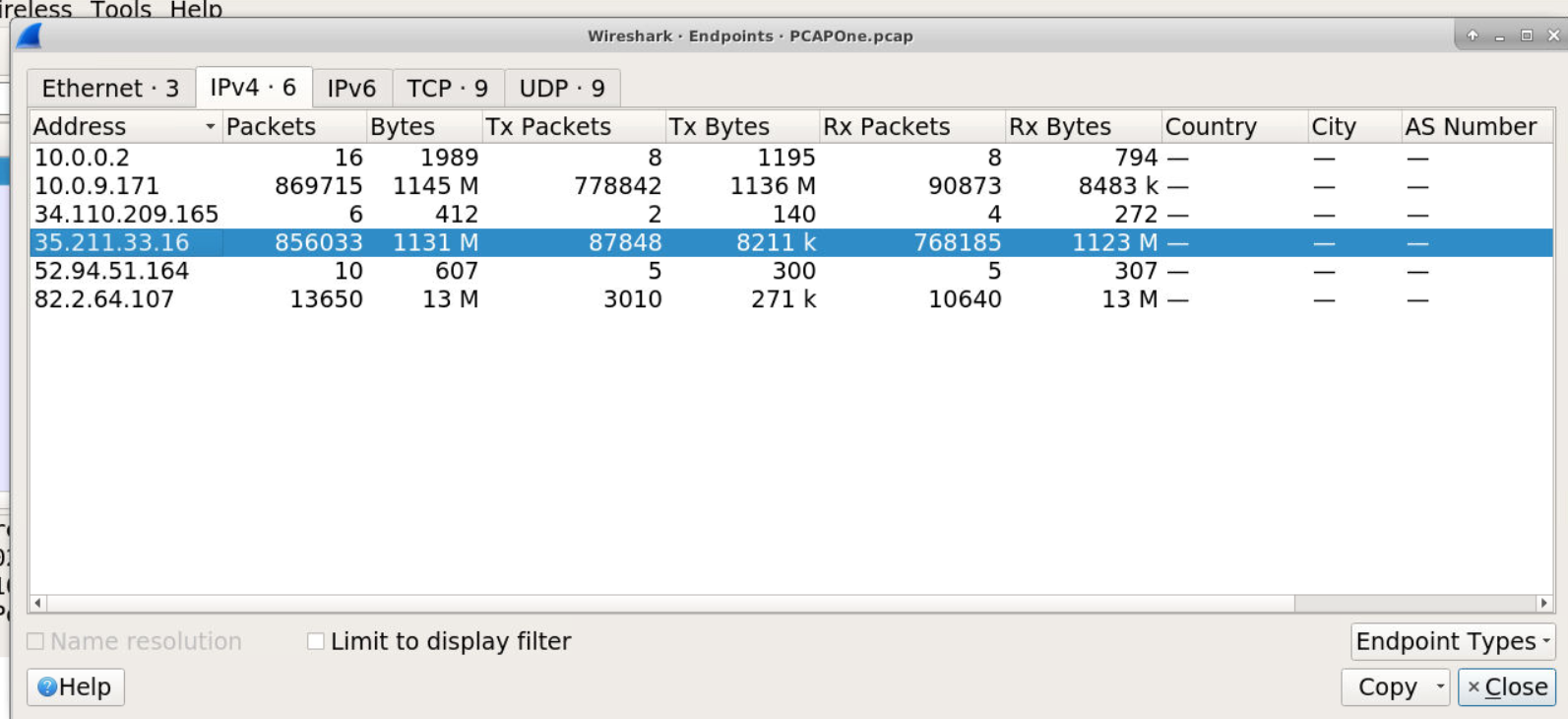
Calculation:
Tx Bytes: 8211 k
Rx Bytes: 1123 M
Total: ~1131 M
Answer: 1131 M
🌐 PCAP Two: Malware Infrastructure Identification
Question 3: Malware Family Attribution
Review the IPs the infected system has communicated with. Perform OSINT searches to identify the malware family tied to this infrastructure (Format: MalwareName)
Analysis:
Identified remote IPs in PCAP Two and conducted VirusTotal research for historical attribution.
Methodology:
- Extracted unique destination IPs from conversations
- Performed VirusTotal lookups on each IP
- Reviewed “Communicating Files” section for malware samples
- Cross-referenced detection names across multiple samples
Key IP Investigated: 31.184.253.165
VirusTotal Findings:
- Multiple malicious executables communicating with this IP
- Consistent detection across vendors
- Historical malware family attribution
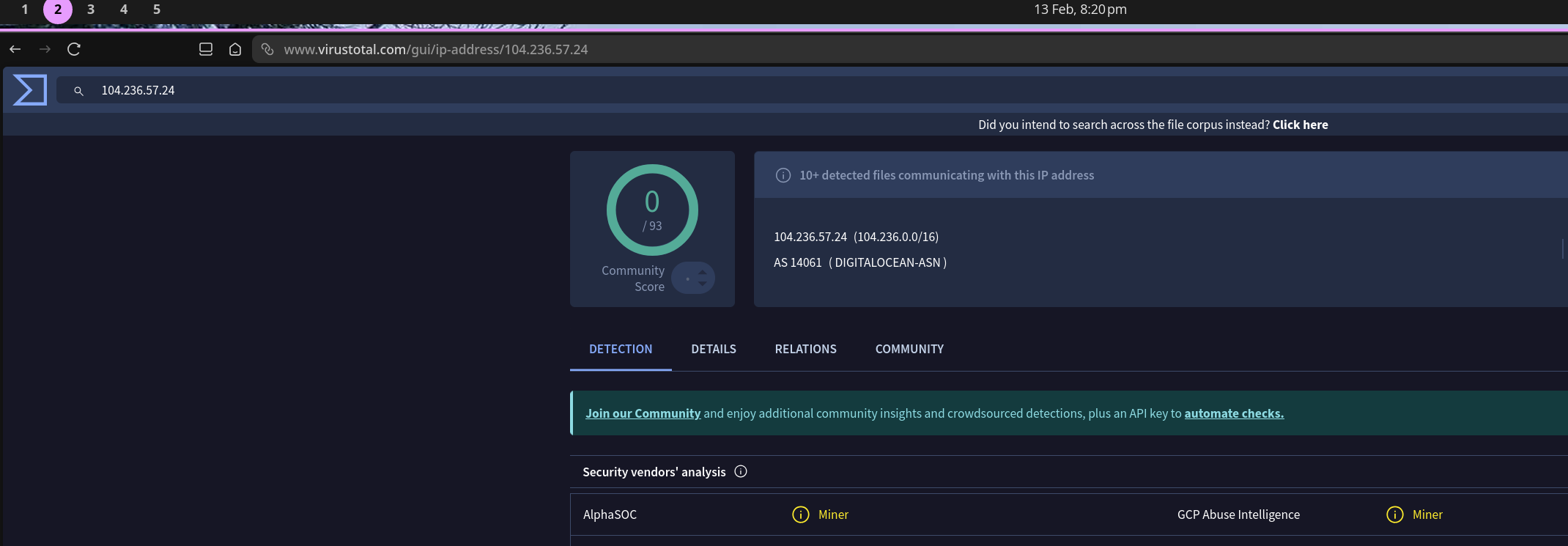
Answer: Trickbot
🔎 PCAP Three: Unusual Port Communications
Question 4: ASN Attribution
Review the two IPs that are communicating on an unusual port. What are the two ASN numbers these IPs belong to? (Format: ASN, ASN)
Analysis:
Identified non-standard port communications and performed ASN lookups.
Methodology:
- Reviewed port statistics to find unusual ports
- Identified IPs communicating on port 8080
- Performed WHOIS/VirusTotal lookups for ASN information
IP 1: 194.233.171.171
- ASN: 63949 (Akamai Connected Cloud)
IP 2: 104.236.57.24
- ASN: 14061 (DIGITALOCEAN-ASN)
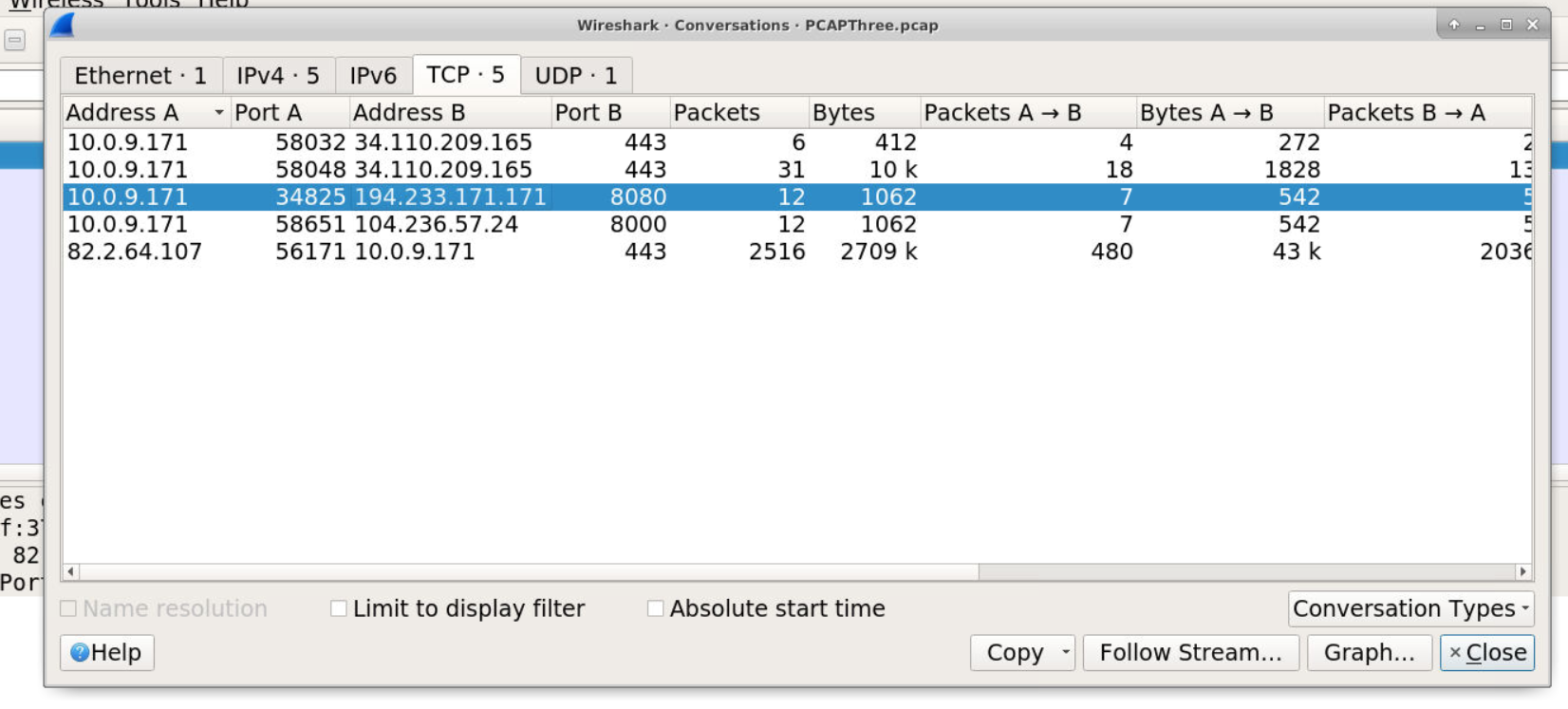
Answer: 63949, 14061
Question 5: Malware Category Attribution
Perform OSINT checks. What malware category have these IPs been attributed to historically? (Format: MalwareType)
Analysis:
Conducted deeper VirusTotal analysis on identified IPs.
IP: 104.236.57.24 - VirusTotal Results:
- Detection Tags:
- ⚠️ AlphaSOC: Miner
- ⚠️ GCP Abuse Intelligence: Miner
- Communicating Files: Multiple cryptocurrency mining executables
- Historical Activity: Consistent mining pool attribution

Conclusion: Infrastructure historically associated with cryptomining operations.
Answer: Miner
Question 6: MITRE ATT&CK Technique
What ATT&CK technique is most closely related to this activity? (Format: TXXXX)
Analysis:
Mapped observed cryptomining behavior to MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Observed Behavior:
- Cryptocurrency mining activity
- Resource hijacking for profit
- Victim system resources consumed for mining operations
MITRE ATT&CK Research:
Technique: T1496 - Resource Hijacking
Description:
“Adversaries may leverage the resources of co-opted systems to complete resource-intensive tasks, which may impact system and/or hosted service availability.”

Answer: T1496
📡 PCAP Four: DNS TXT Record Analysis
Question 7: TXT Query Timing (Seconds Since Capture Start)
Go to View > Time Display Format > Seconds Since Beginning of Capture. How long into the capture was the first TXT record query made? (Format: X.xxxxxx)
Analysis:
Configured Wireshark time display and located first DNS TXT query.
Methodology:
- View → Time Display Format → Seconds Since Beginning of Capture
- Applied filter:
dns.qry.type == 16(TXT records) - Identified first packet in results
First TXT Query:
Time: 2.047649 seconds
Frame: 875
Query: mlckdhokhvhtcmevvcqbggcviwxqim.sandbox.alphasoc.xyz
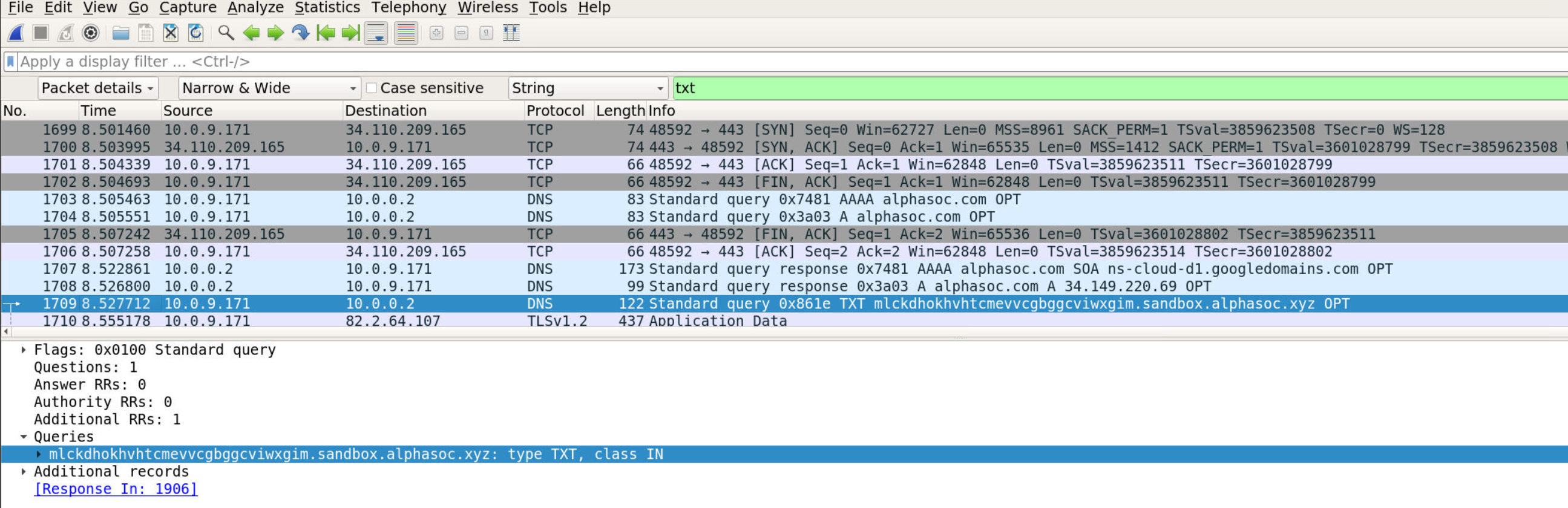
Answer: 8.527712
Question 8: TXT Query Timestamp (UTC)
Go to View > Time Display Format > UTC Date and Time of Day. What is the date and timestamp? (Format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS)
Analysis:
Changed time display format to UTC and captured absolute timestamp.
Methodology:
- View → Time Display Format → UTC Date and Time of Day
- Located same TXT query packet (Frame 875)
- Noted UTC timestamp
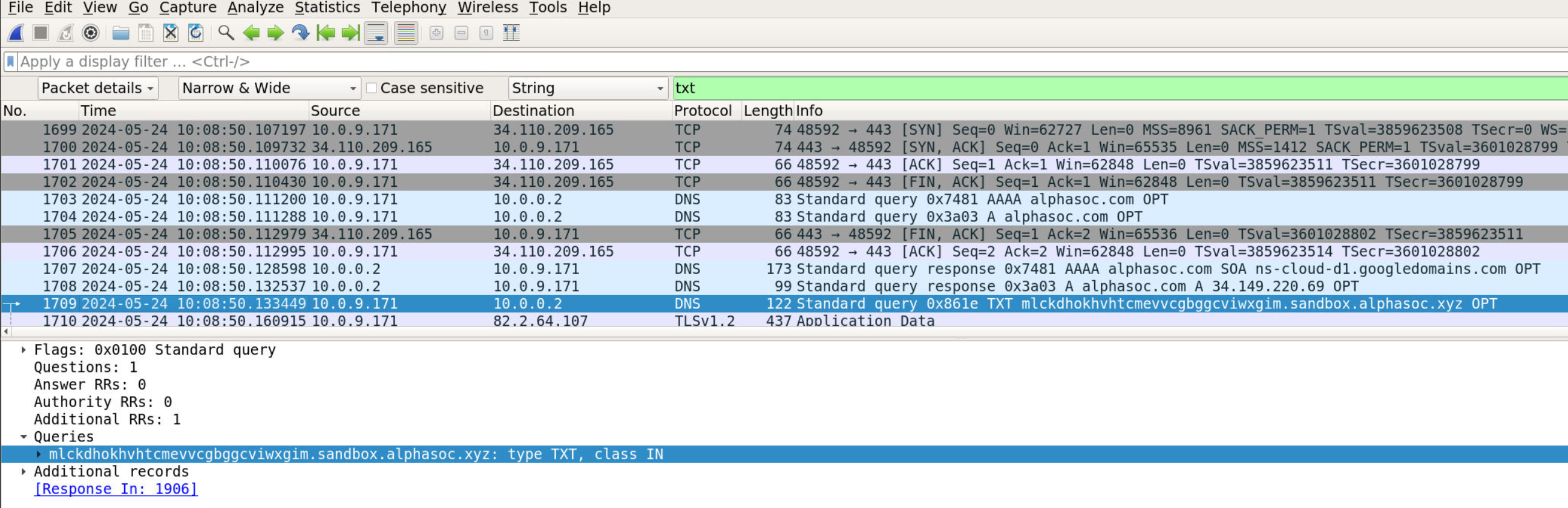
Answer: 2024-05-24 10:08:50
Question 9: MITRE ATT&CK Subtechnique
What is the ATT&CK subtechnique relating to this activity? (Format: TXXXX.xxx)
Analysis:
Identified DNS TXT record usage as a C2 channel and mapped to specific subtechnique.
Observed Behavior:
- DNS TXT queries for command and control
- Encoded data in DNS requests
- Application layer protocol abuse
MITRE ATT&CK Research:
Subtechnique: T1071.004 - Application Layer Protocol: DNS
Description:
“Adversaries may communicate using the Domain Name System (DNS) application layer protocol to avoid detection/network filtering by blending in with existing traffic.”

Answer: T1071.004
✅ Lab Completion
Final Results:
- ✓ All 9 questions answered correctly (27/27 points)
- ✓ Identified SSH data exfiltration (1131 M transferred)
- ✓ Attributed Pony malware family via OSINT
- ✓ Discovered cryptomining infrastructure (Miner category)
- ✓ Mapped to MITRE ATT&CK framework (T1496, T1071.004)
- ✓ Demonstrated multi-PCAP correlation skills
📊 MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
| Technique ID | Technique Name | Observed Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| T1071.004 | Application Layer Protocol: DNS | DNS TXT queries for C2 communication |
| T1496 | Resource Hijacking | Cryptomining infrastructure and miner attribution |
| T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | SSH data transfer to remote IP |
| T1071.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | HTTP/HTTPS traffic to mining pools |
🎓 Key Takeaways
Technical Skills Demonstrated
PCAP Analysis:
- Multi-file PCAP investigation and correlation
- SSH traffic analysis and data volume calculation
- DNS query inspection (TXT records)
- Wireshark statistics and conversation analysis
- Time display format configuration
Threat Intelligence:
- VirusTotal OSINT research
- ASN attribution and WHOIS lookups
- Historical malware family identification
- IOC correlation across multiple sources
Framework Application:
- MITRE ATT&CK technique mapping
- Subtechnique identification
- Understanding attacker TTPs across multiple stages
SOC Analyst Perspective
Detection Opportunities:
- Monitor for large SSH data transfers to external IPs
- Alert on connections to known malware/mining infrastructure
- Detect suspicious DNS TXT queries (especially to random subdomains)
- Track ASN reputation for outbound connections
- Correlate multiple indicators across timeframes
Investigation Workflow:
- Identify anomalies - Unusual ports, large transfers, suspicious domains
- Extract IOCs - IPs, domains, ports, protocols
- Enrich with OSINT - VirusTotal, ASN lookups, malware databases
- Map to framework - ATT&CK techniques for context
- Document findings - Timeline, evidence, conclusions
Lessons Learned:
- Multi-PCAP investigations require correlation across files
- OSINT is critical for attribution and historical context
- Time display format matters for incident reporting
- Understanding both techniques and subtechniques provides deeper analysis
- Statistical analysis (data volume) can reveal exfiltration
🔗 Investigation Artifacts
IOCs Identified:
| Indicator Type | Value | Context |
|---|---|---|
| IPv4 | 35.211.33.16 | SSH data exfiltration destination |
| IPv4 | 31.184.253.165 | Pony malware C2 infrastructure |
| IPv4 | 194.233.171.171 | Mining infrastructure (AS 63949) |
| IPv4 | 104.236.57.24 | Mining infrastructure (AS 14061 - Miner tagged) |
| Domain | mlckdhokhvhtcmevvcqbggcviwxqim.sandbox.alphasoc.xyz | DNS TXT C2 query |
| Port | 22 (SSH) | Data exfiltration channel |
| Port | 8080 | Unusual port communication |
| Data Volume | 1131 M | Total SSH transfer volume |
| Malware Family | Trickbot | Stealer/information theft malware |
Timeline:
2024-05-24 10:08:50 UTC- First DNS TXT query (8.527712s into capture)
```